This article will cover how to connect to a physical database (SQL) using Power BI that exists within a local network. Within this article, the following objectives will be taken into account:
- Create and publish a file (.pbix) that imports information from a database (BDD).
- Set up and tune datasets in Power BI for connection to a SQL server through a gateway.
- Set up an updatable schedule to ensure the dataset has real-time information.
- Review of updated history to analyze the results of past cycles.
Create a Power BI file connected to a database
In Power BI either the web or desktop version select Get Data and then choose SQL Server Database click Connect
Enter the server and database names, be sure that the connection mode is set to Import
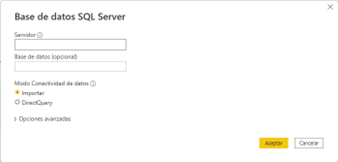
FIGURE 1
Verify your credentials and select connect
Once the connection is made, you will be able to see the tables that are inside the database, and you will have to select the one that interests you most. Once you have chosen the tables of click on Load
In the Power BI reports view, in the visualizations pane, choose the chart that best fits your needs and project the information you want.
Save the report where it needs to be saved, then publish it to your workspace.
Connect a dataset to a SQL database
In the Power BI desktop app, you can connect directly to a physical database, but this service requires a gateway that acts as a bridge between the cloud and its physical network. Here’s how the connection can be made to you.
Sign into your Microsoft account on the Power BI page, at the top right, on the gear icon click and select settings, then find the Datasets tab and click Gateway connection.
In the case of not having the plug-in installed, it installs it. Make sure you have the correct database credentials; without this information the gateway will not function properly.

FIGURE 2
On the Gateway administration page, on the Data Source Configuration tab, select the gateway and click Settings. A window will open with some fields in which you must enter the following information according to your environment:
| Option | Value |
| Data source name | Any name |
| Data source type | SQL Server |
| Server | The name of the SQL server (This must be the exact name you put in the Power BI app). |
| Database | The name of the database (This must be the exact name you put in the Power BI app.) |
| Authentication method | Basic Windows. |
| Username | The user you use to connect to the SQL server. |
| Password | The password you use to connect to the SQL server. |
TABLE 1 (DATA SOURCE VALUE)
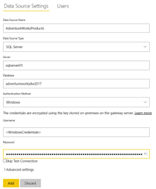
FIGURE 3
In the dataset tab, according to Fig. 2 select the gateway that is connected. Click apply.
Configuring an update program
Once a connection to a dataset has been established through a gateway, setting up a schedule update is the best way to make a report. This helps you to have real-time reports with the latest information.
In the section of my workspace select dataset, select a file then click on the three ellipsis (…) Choose Settings and go to Scheduled Update and Configure. If you want, you can leave the box checked to receive emails for update errors. Once all configuration parameters are set, select Apply.

FIGURE 4
Additionally, it is mentioned that you can configure up to 8 times if the data set is shared, or up to 48 in Power BI Premium. These times serve to update the report; however, updates occur within 15 minutes.
CONCLUSIONS
- Power BI is a tool that can get information from a SQL database with different types of authentications.
- Power BI can update reports automatically providing real-time information.
- You can monitor the updates that are developed as the file changes.
- Full-featured use of Power BI requires a license.
- You can link not only database for a real-time update, but you can also link document in the cloud or on the local PC. These documents can be Access databases, Excel spreadsheets, tables within Excel, data flows, web, and text or CSV files.
